Blood Clot in Prostate
Welcome to our in-depth examination of a critical yet often overlooked health concern: blood clots in the prostate. Although this condition is relatively rare, it can lead to significant health complications for men, particularly as they advance in age.
In this article, we will explore the nature of blood clots, how they develop specifically in the prostate, and the potential health ramifications. We’ll also discuss the various symptoms associated with this condition, providing a clear guide on what to watch for.
Most importantly, we will cover the latest treatment options available and offer practical advice on preventive measures to help maintain prostate health and prevent the occurrence of blood clots.
Join us as we uncover the essential aspects of managing and understanding this important men’s health issue.
Contents
Understanding the Prostate
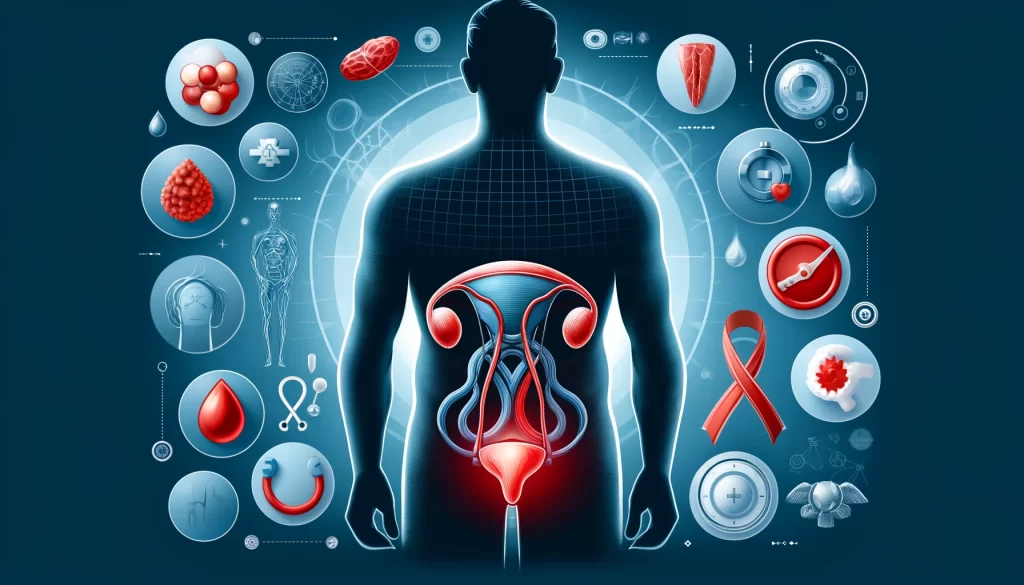
Anatomy of the Prostate
The prostate gland is a crucial, small, walnut-shaped organ uniquely positioned below the bladder in men. This gland encases part of the urethra—the duct responsible for the passage of urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The location and structure of the prostate are vital for its functionality, impacting both the urinary and reproductive systems. Its intimate association with the urethra explains its significant role in urinary control, and its proximity to other reproductive organs underscores its importance in sexual health.
Functions of the Prostate
The primary role of the prostate is to produce and secrete prostate fluid, one of the main components of semen. The fluids secreted by the prostate are slightly alkaline, which helps to neutralize the acidic environment of the vagina, thereby increasing the viability and lifespan of sperm. This fluid also contains enzymes, proteins, and minerals that are crucial for the fertility and motility of sperm. In addition to its reproductive functions, the prostate also contains muscle fibers that help to expel semen during ejaculation and control the flow of urine. These dual roles make the prostate an essential organ for both urinary function and reproductive capacity.
What is a Blood Clot?
Definition and Explanation
A blood clot, medically referred to as a thrombus, is a cluster of blood cells and coagulants that form a gel-like mass within the bloodstream or an organ. The primary components of a blood clot are platelets—small blood cells that rush to a site of injury—and fibrin, a fibrous protein that interlaces to form a mesh that traps blood cells. This process is essential for stopping bleeding and initiating the healing process after tissue damage. However, when these clots form inappropriately or persist within the bloodstream or organs like the prostate, they can lead to complications rather than healing.
Causes of Blood Clots
Blood clots in the prostate, specifically, can form for several reasons, each linked to broader health issues. The primary causes include:
- Injury: Trauma to the pelvic area can lead to localized clotting as the body attempts to heal the injured tissues. This is common in sports injuries or after surgeries.
- Immobility: Extended periods of immobility, such as those experienced during long flights or bed rest after surgery, can reduce blood flow and increase the risk of clot formation.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions such as hypercoagulability, where the blood has an increased tendency to clot, can predispose individuals to thrombus formation. Diseases like cancer and inflammatory conditions also enhance clotting tendencies due to changes in the body’s biochemistry and immune responses.
- Age and Hormonal Changes: As men age, changes in hormone levels, particularly a reduction in testosterone, can affect blood flow and vascular health, increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate the risk of clot formation by impacting cardiovascular health and blood circulation.
Blood Clots in the Prostate
How Blood Clots Affect the Prostate
When blood clots form in the prostate, they can lead to several detrimental effects on urinary and reproductive health. The presence of a clot can obstruct the flow of urine by physically blocking the urethra or by causing swelling that narrows the urinary passage. This obstruction can result in painful, difficult, or incomplete urination, and in severe cases, can cause acute urinary retention—a medical emergency where a person is unable to urinate at all. Additionally, the increased pressure from retained urine can lead to further complications, such as bladder damage or infections.
Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of a blood clot in the prostate are often alarming and prompt immediate concern. These include:
- Painful Urination: A burning or stinging sensation during urination can indicate the presence of a clot.
- Difficulty Urinating: Straining to urinate or experiencing a weak urine stream may suggest partial blockage by a clot.
- Pelvic Discomfort: General pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, especially when combined with urinary symptoms, is a significant indicator.
Recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for timely intervention and can prevent the progression of more severe complications.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Techniques
The diagnosis of a blood clot in the prostate involves several steps:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may perform a digital rectal exam (DRE) to assess for abnormalities in the size, shape, or texture of the prostate.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound can be particularly useful in visualizing the internal structure of the prostate gland and identifying areas where blood flow may be obstructed by clots.
- Biopsy: In cases where a tumor or cancer is also suspected, a biopsy may be performed to differentiate between benign and malignant causes of symptoms.
These diagnostic tools are essential for accurately identifying the presence of clots and determining the best course of treatment.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of blood clots in the prostate is paramount in managing the condition effectively. Identifying clots early can drastically reduce the risk of severe complications, such as bladder damage or chronic urinary problems. Additionally, early treatment can alleviate symptoms quickly and improve overall quality of life. Regular medical check-ups and being attuned to the symptoms of prostate issues are key strategies in ensuring prompt detection and treatment.
Treatment Options

Medical Treatments
Effective management of blood clots in the prostate often requires a combination of medical treatments which include:
- Medications: Anticoagulants (blood thinners) may be prescribed to help dissolve the clot and prevent new clots from forming. Anti-inflammatory medications can also be used to reduce swelling and alleviate pain associated with the clot.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where the clot is large or causing significant obstruction or symptoms, surgical removal might be necessary. Procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) are performed to remove part of the prostate gland to relieve symptoms.
- Catheterization: If acute urinary retention occurs, a catheter may be temporarily used to drain the bladder and relieve pressure until more definitive treatment can be applied.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Home Care
Alongside medical interventions, certain lifestyle modifications can significantly impact the recovery and overall health of the prostate:
- Increasing Fluid Intake: Drinking more fluids, especially water can help flush the urinary tract and aid in the prevention of further clot formation.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity improves blood flow and reduces the risk of clot formation due to prolonged immobility.
- Dietary Changes: Incorporating a diet low in saturated fats and rich in vegetables, fruits, and fibers can help maintain not only prostate health but also cardiovascular health, which is crucial in preventing clot formation.
Prevention
Preventive Measures
To prevent the occurrence or recurrence of blood clots in the prostate, certain preventive strategies can be highly effective:
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine health screenings and prostate exams can help detect issues before they develop into serious conditions.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a known risk factor for many health issues, including blood clots. Keeping a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
- Avoiding Prolonged Immobility: For individuals in sedentary jobs or those who travel frequently, taking breaks to move around and stretch can help maintain good circulation and reduce clot risks.
Role of Diet and Exercise
A well-balanced diet and regular physical activity are not just beneficial for overall health—they play a specific role in blood clot prevention:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3s, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help reduce blood viscosity and improve cardiovascular health.
- Low Saturated Fats: A diet low in saturated fats can prevent the buildup of cholesterol in arteries, which is a contributing factor to clot formation.
- Routine Exercise: Regular exercise helps improve blood flow and can significantly reduce the risk of blood clots. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for those with prostate health concerns.
Long-Term Management
Monitoring and Managing Health
Maintaining prostate health over the long term requires an integrated approach that combines medical oversight with lifestyle management:
- Regular Medical Screenings: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential. These may include prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, which can help detect prostate abnormalities early. Digital rectal exams (DRE) are also recommended annually for men over the age of 50 or at a younger age if risk factors are present.
- Lifestyle Management: Adopting a lifestyle that supports overall health can significantly impact prostate health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep. It also involves managing stress effectively, as high-stress levels can adversely affect prostate health and immune function.
- Medication Management: For those on medications for prostate health or related conditions, regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure that treatments remain effective and are adjusted as needed to suit changes in condition or side effects.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Knowing when to seek medical advice is crucial for managing prostate health effectively:
- Onset of Symptoms: Any new or worsening symptoms related to urination or sexual function should prompt a consultation. These can include changes in urinary frequency, pain during urination, blood in the urine or semen, painful ejaculation, or erectile dysfunction.
- Changes in Health Status: Significant changes in overall health, such as unexpected weight loss, and persistent pain in the lower back, hips, or thighs, may require a reevaluation of prostate health.
- Routine Follow-Ups: Even in the absence of symptoms, routine follow-ups based on the doctor’s recommendations are vital. These visits can help catch potential problems early and adjust preventive strategies as needed.
- Post-Treatment Monitoring: After any treatment for prostate conditions, regular follow-ups to monitor recovery and ensure that the condition has been effectively managed are important. These visits can also help in the early detection of any recurrence.
ALSO READ: FlowForce Max SCAM – Is It Fake OR Legit Prostate Shrinking Chew Candy?
Conclusion – Blood Clot in Prostate
Understanding the risks, symptoms, and treatment options for blood clots in the prostate is vital for maintaining men’s health, especially as they advance in age. This condition, while potentially severe, can be effectively managed with the right combination of medical intervention, lifestyle changes, and regular health monitoring.
By staying informed about the early signs and potential complications of blood clots in the prostate, men can take proactive steps to seek timely medical advice. Education on this topic also empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, advocating for necessary tests and treatments that can prevent the progression of symptoms.
Moreover, adopting a healthy lifestyle that supports good circulation and prostate health can play a significant role in prevention. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding factors that contribute to poor vascular health, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Ultimately, the goal is not just to manage or treat an existing condition but to enhance overall well-being and quality of life. With appropriate care and vigilance, the impact of blood clots in the prostate can be significantly minimized, allowing men to lead healthier, more active lives.
blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate, blood clot in prostate,
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the most common symptoms of a blood clot in the prostate?
The most typical symptoms of a blood clot in the prostate include difficulty urinating, a painful or burning sensation during urination, and pelvic or lower back pain. These symptoms can be similar to those of other prostate conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer, making it crucial to seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis.
-
How can lifestyle changes affect the risk of developing blood clots in the prostate?
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact the risk of developing blood clots in the prostate by improving blood flow and overall vascular health. Key changes include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These actions help reduce the risk of blood clot formation not only in the prostate but throughout the entire body.
-
What are the potential complications of untreated blood clots in the prostate?
If left untreated, blood clots in the prostate can lead to serious complications, including acute urinary retention, where one cannot urinate at all, which is a medical emergency. Chronic urinary retention can also develop, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections and possibly kidney damage. Additionally, persistent blood clots can cause chronic pelvic pain and significantly impact the quality of life.
-
How often should one undergo prostate examinations?
The frequency of prostate examinations can vary based on individual risk factors, but generally, men over the age of 50 should consider having an annual prostate exam, including a digital rectal exam (DRE) and possibly a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. Men with higher risk factors, such as a family history of prostate cancer, may be advised to start screening earlier and more frequently.
-
Are there any natural remedies or supplements that help in preventing blood clots in the prostate?
While no natural remedies or supplements can replace medical treatment for blood clots, some may help reduce the risk of clot formation. Supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to improve cardiovascular health and reduce blood clotting, may be beneficial. Additionally, herbal supplements like ginger and turmeric have natural anti-inflammatory properties and may help improve blood flow. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you are already on medication for blood clotting or other health issues.