Prostate Cancer Symptoms and Prostate cancer are prevalent health concerns for men worldwide. As the second most common male cancer, it accounts for many new cancer cases yearly [9]. Prostate cancer often remains undetected in the early stages due to a lack of noticeable signs or symptoms.
However, as the disease progresses, various symptoms may appear, significantly impacting a man’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms associated with prostate cancer is essential for early detection and appropriate treatment.
This article will explore the symptoms of both early and advanced stages of prostate cancer and discuss the importance of screening and detection to improve treatment outcomes and overall prognosis.
Contents
What is the Prostate?
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland in the male reproductive system. It is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum, surrounding the urethra – the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis.
The prostate gland’s primary function is to produce a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm, which is then mixed with sperm during ejaculation to form semen. The prostate also contains smooth muscles that help expel semen during ejaculation.
5 Early Stage Prostate Cancer Symptoms
During the early stages of prostate cancer, symptoms may be subtle or non-existent. However, as the tumor grows, it can exert pressure on the surrounding tissue and urethra, leading to noticeable urinary symptoms. Some of the early-stage prostate cancer symptoms include:
1) Difficulty urinating
Men with early-stage prostate cancer may find it challenging to start urination or may experience a delay in urine flow. This issue can be due to the tumor’s pressure on the urethra[2].
2) The weak or interrupted flow of urine
A weak or interrupted flow of urine can be another symptom of early-stage prostate cancer. The tumor may partially obstruct the urethra, causing the urine flow to become more vulnerable or less consistent[2].
3) Frequent urination, especially at night
Men with prostate cancer may experience an increased need to urinate, particularly at night. This increased frequency can result from the growing tumor pressing against the bladder or urethra, causing the sensation of needing to empty the bladder more often[2].
4) Trouble emptying the bladder
Prostate cancer may make it difficult to empty the bladder fully. The tumor’s presence can obstruct the flow of urine or create a sensation of pressure in the bladder, making it challenging to feel like the bladder is empty even after urinating[2].
5) Urinary urgency
Men with early-stage prostate cancer may also experience a sudden, intense need to urinate. This urgency can be a result of the tumor’s impact on the bladder and urethra, causing increased sensitivity and the sensation of needing to urinate immediately[2].
Early detection of prostate cancer can lead to more effective treatment options and improved outcomes. It is crucial to remember that these symptoms can also be caused by other, less severe conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis.
However, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
7 Advanced Stage Prostate Cancer Symptoms
When prostate cancer progresses to advanced stages, the symptoms become more pronounced and can significantly impact a man’s daily life. Cancer may spread to other body parts, leading to additional symptoms.
Some of the advanced-stage prostate cancer symptoms include:
1) Blood in the urine or semen
As prostate cancer advances, blood may appear in the urine or semen. This symptom can be due to the tumor invading the blood vessels or tissues around the prostate[1].
2) Pain in the hips, back, chest, or other areas
Advanced prostate cancer can spread to the bones, causing pain in various areas, such as the hips, back, or chest. Bone pain can result from cancer damaging and weakening the bone structure[3].
3) Weakness or numbness in the legs or feet
As cancer spreads, it may press on the spinal cord, leading to weakness or numbness in the legs or feet. This symptom can significantly affect mobility and daily activities[3].
4) Lower extremity symptoms
Advanced prostate cancer can cause pain or stiffness in the lower back, hips, or upper thighs. Additionally, swelling may occur in the lower extremities due to cancer’s impact on the lymphatic system and circulation[4].
5) Painful ejaculation and decreased volume of ejaculation
Men with advanced prostate cancer may experience painful ejaculation and a decrease in the volume of ejaculation. These symptoms can be due to the tumor invading the prostate gland and affecting the production of seminal fluid[7].
6) Erectile dysfunction
The ability to maintain an erection may become impaired due to advanced prostate cancer. This issue can be a result of the tumor invading nerves responsible for erections or due to the cancer treatment itself[7].
7) Loss of libido (sex drive)
Prostate cancer and its treatment may cause a loss of interest in sex due to physical discomfort or side effects from cancer treatments[8].
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional as soon as possible. Early intervention and treatment can help manage the symptoms and improve the overall quality of life for men with advanced-stage prostate cancer.
4 Prostate Cancer Screening and Detection
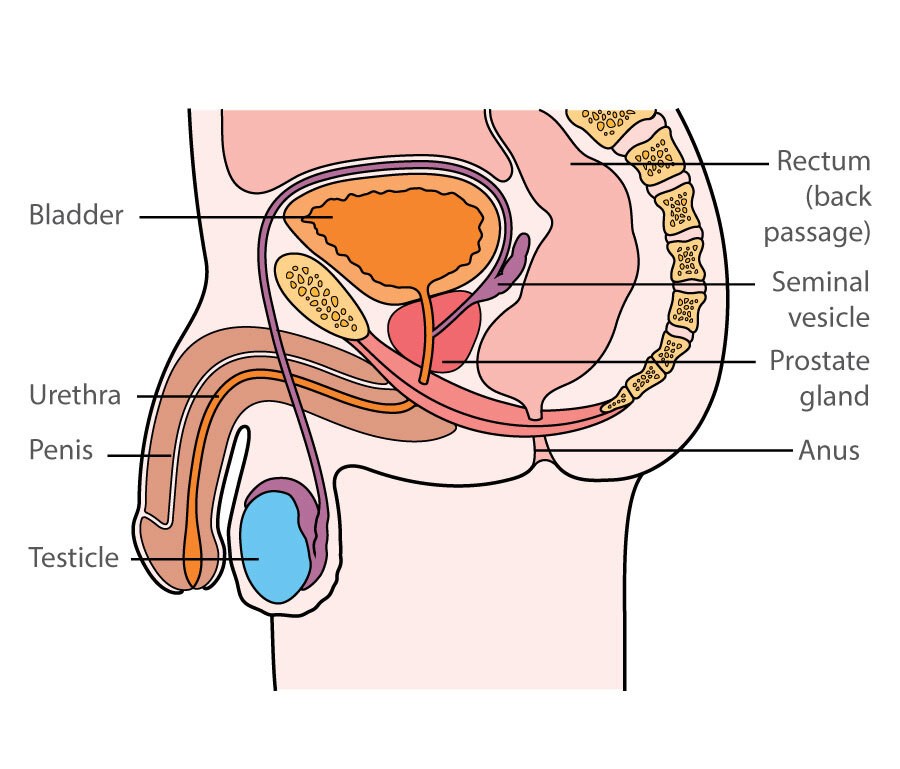
Screening for prostate cancer in healthy men without symptoms is a controversial topic, as there is debate among medical organizations regarding the benefits of testing compared to the potential risks[5].
Nonetheless, early detection is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and overall prognosis. The following methods are commonly used for prostate cancer screening and detection:
1) Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
During a DRE, a healthcare professional inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for any abnormalities or enlargement in the prostate gland. While this test can be uncomfortable, it is a quick and straightforward method for detecting potential issues.
2) Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
The PSA test is a blood test that measures the level of prostate-specific antigens in the blood. Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate cancer but can also be a sign of other conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis.
Therefore, it is essential to consider other factors, such as age and family history, when interpreting PSA test results.
3) Biopsy
If the DRE or PSA test indicates a potential issue, a biopsy may be performed. Small prostate tissue samples are collected and analyzed during a biopsy to determine if cancer cells are present.
The biopsy can provide a definitive diagnosis of prostate cancer and help healthcare professionals assess the aggressiveness of cancer.
4) Imaging tests
If a biopsy confirms the presence of prostate cancer, imaging tests may be used to determine the extent of the tumor and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. Standard imaging tests include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and bone scans.
Early detection of prostate cancer can lead to more effective treatment options, improved outcomes, and a better quality of life. Most medical organizations encourage men in their 50s to discuss the pros and cons of prostate cancer screening with their healthcare providers[5].
This discussion should consider individual risk factors, such as age, family history, and race, to decide whether to undergo screening.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer is a significant health concern for men worldwide, with many cases often remaining undetected in the early stages due to a lack of noticeable symptoms.
As cancer progresses, various symptoms may arise, ranging from urinary issues to pain and discomfort in different body parts. Understanding the symptoms associated with early and advanced prostate cancer stages is crucial for timely detection and appropriate treatment.
Screening for prostate cancer remains controversial, but discussing the pros and cons of screening with a healthcare professional is vital for making informed decisions about testing.
Early detection of prostate cancer through digital rectal examination, PSA tests, and biopsies can lead to more effective treatment options, improved outcomes, and a better quality of life for affected individuals.
If you experience any symptoms related to prostate cancer or have concerns about your risk, consult with a healthcare provider to ensure timely evaluation and diagnosis.
FAQs
What are the early symptoms of prostate cancer?
Early-stage prostate cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms. However, some men may experience urinary issues such as difficulty starting urination, weak or interrupted urine flow, frequent urination, especially at night, or trouble emptying the bladder [2].
What are the symptoms of advanced prostate cancer?
Advanced prostate cancer symptoms may include blood in urine or semen, pain in hips, back, or chest due to cancer spreading to bones, weakness or numbness in legs or feet, lower extremity symptoms like pain or stiffness, painful ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, and loss of libido (sex drive)[3, 4, 7, 8].
What are the standard methods for prostate cancer screening and detection?
The standard methods for prostate cancer screening and detection include digital rectal examination (DRE), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, biopsy, and imaging tests like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) scans, and bone scans[5].
When should men start discussing prostate cancer screening with their healthcare providers?
Most medical organizations recommend that men in their 50s discuss the pros and cons of prostate cancer screening with their healthcare providers. The discussion should consider individual risk factors such as age, family history, and race[5].
Can prostate cancer be detected without symptoms?
Yes, many cases of prostate cancer are detected through screening tests like digital rectal examinations and PSA tests in men without symptoms. Early detection of prostate cancer can lead to more effective treatment options and improved outcomes[10].
Reference
1.https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20353087
2.https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/prostate/basic_info/symptoms.htm
3.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostate-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-symptoms.html
5.https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353093
7.https://health.clevelandclinic.org/warning-signs-of-prostate-cancer/
8.https://www.webmd.com/prostate-cancer/guide/understanding-prostate-cancer-symptoms
9.https://www.healthline.com/health/prostate-cancer-stages
10.https://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostate-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/how-diagnosed.html