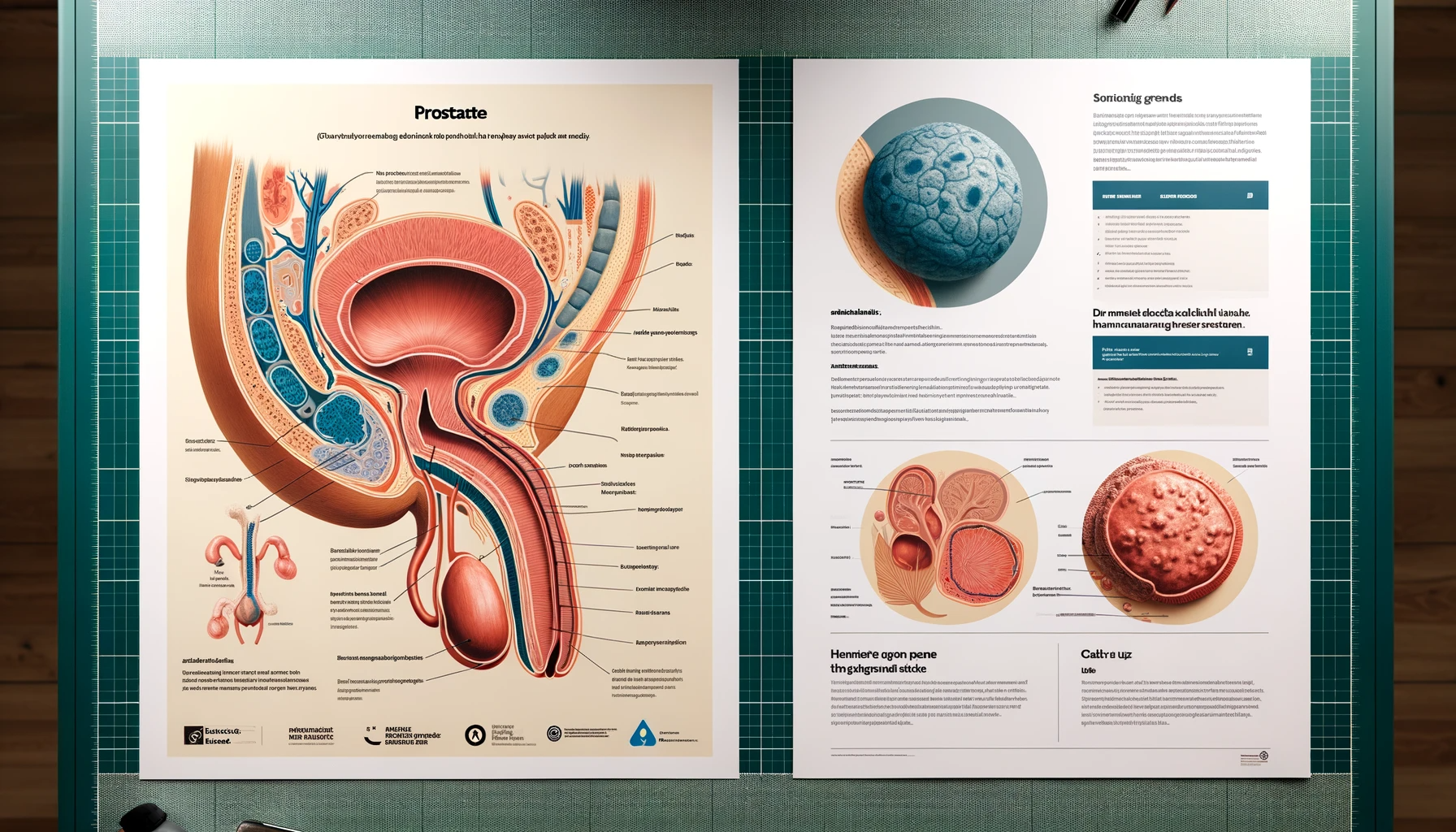
Prostate Removal Side Effects
Prostate removal, medically known as prostatectomy, is a significant surgical procedure often necessitated by conditions like prostate cancer. While it can be a life-saving intervention, it’s crucial to understand the potential side effects that may follow.
This article delves into the various aspects of post-prostate removal life, offering a blend of medical expertise and practical advice.
Contents
The Necessity of Prostate Removal: Medical Context
Prostate removal, clinically known as a prostatectomy, is a surgical procedure primarily necessitated by prostate cancer, one of the most common cancers in men. Understanding the medical context and necessity for this procedure is crucial for patients and their families as they navigate through the decision-making and preparation process.
1. Why Prostate Removal is Considered
- Cancer Containment: The primary reason for prostate removal is to eliminate or contain prostate cancer. When cancer is localized or confined within the prostate, removal of the gland can be a curative approach.
- Preventing Spread: In cases where there’s a high risk of cancer spreading to other parts of the body, prostate removal becomes a proactive measure to prevent metastasis.
- Symptom Relief: For some patients, an enlarged prostate due to cancer can cause significant urinary symptoms. Removal of the prostate can alleviate these symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: The decision for prostate removal is often based on a combination of factors including the patient’s age, overall health, stage of cancer, and personal preferences. It’s a tailored approach, considering the aggressiveness of the cancer and potential side effects.
2. Understanding the Risks and Benefits
- Potential for Cure: In many cases, especially when cancer is localized, prostate removal can be a definitive cure.
- Risk of Side Effects: The procedure can lead to side effects such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction. These risks need to be weighed against the potential benefits.
- Psychological Impact: The decision and aftermath of prostate removal can have significant psychological impacts, including anxiety and depression, which need to be addressed as part of the treatment plan.
3. Advancements in Prostate Removal
- Surgical Techniques: Advances in surgical techniques, including robotic-assisted prostatectomy, have improved outcomes and reduced some of the side effects associated with traditional open surgery.
- Precision Medicine: The growing field of precision medicine allows for more personalized approaches to treatment, considering the genetic makeup of the cancer and the patient.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Post-surgery, patients undergo regular monitoring, which includes PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) testing to check for signs of cancer recurrence.
4. Making an Informed Decision
- Consultation with Specialists: Patients must consult with urologists, oncologists, and possibly a radiologist to understand all treatment options.
- Understanding Individual Health Context: Each patient’s health status, including age, overall health, and specific characteristics of their cancer, plays a critical role in the decision-making process.
- Considering Quality of Life: Discussions about life post-surgery, including potential changes in urinary and sexual function, are essential. Quality of life considerations are as important as the treatment of cancer itself.
Prostate Surgery Techniques and Approaches

Prostate surgery, a critical treatment for prostate cancer and other prostate-related issues, has evolved significantly over the years. The choice of surgical technique depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s expertise. Here, we’ll discuss the most common techniques and approaches used in prostate surgery.
1. Traditional Open Surgery
- Retropubic Surgery: This approach involves making an incision in the lower abdomen to access the prostate. It’s often used when lymph nodes need to be removed for cancer evaluation.
- Perineal Surgery: An incision is made in the perineum, the area between the anus and scrotum. This approach can be less invasive but may not allow for lymph node removal.
2. Minimally Invasive Techniques
- Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: This technique involves small incisions and the use of a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) to guide the surgery. It’s less invasive, leading to potentially shorter hospital stays and recovery times.
- Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: An advanced form of laparoscopic surgery, it uses robotic arms controlled by the surgeon. This approach provides more precision and flexibility than traditional laparoscopic surgery.
3. Emerging Techniques and Technologies
- Focal Therapies: These are less invasive options for treating localized prostate cancer, targeting only the cancerous areas of the prostate. Techniques include cryotherapy, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), and laser ablation.
- Image-Guided Surgery: Advanced imaging techniques, like MRI and ultrasound, are increasingly being used to guide surgical procedures, improving precision and outcomes.
4. Choosing the Right Approach
- Patient-Specific Factors: The choice of surgical technique depends on the patient’s age, overall health, stage and grade of cancer, and personal preferences.
- Surgeon’s Expertise: The surgeon’s experience and proficiency with a particular technique also play a crucial role in determining the approach.
- Potential Risks and Benefits: Each technique has its own set of potential risks and benefits, which must be carefully weighed. For instance, minimally invasive techniques may offer quicker recovery but might not be suitable for all types of prostate cancer.
5. Post-Surgery Considerations
- Recovery Time: Recovery varies based on the surgical approach. Minimally invasive surgeries often have shorter recovery times.
- Managing Side Effects: Common side effects like incontinence and erectile dysfunction are addressed differently depending on the surgical technique used.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up is essential regardless of the surgical approach to monitor for potential recurrence of cancer and manage any long-term effects.
10 Prostate Removal Side Effects
Prostate removal, known medically as prostatectomy, is a common treatment for prostate cancer. While it can be life-saving, it’s important to understand the potential side effects that can arise from this surgery. These side effects can vary in severity and duration, depending on the individual and the specific surgical technique used.
1. Urinary Incontinence
- Stress Incontinence: This is the most common type, where coughing, sneezing, or physical activity can cause urine leakage.
- Urge Incontinence: Involves a sudden, intense urge to urinate, followed by an involuntary loss of urine.
- Management: Pelvic floor exercises, medications, and sometimes surgery can help manage incontinence.
2. Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Nerve Damage: ED can occur if the nerves that control erections are damaged during surgery.
- Recovery Time: Nerve-sparing techniques can reduce this risk, but recovery of erectile function can take months or even years.
- Treatment Options: Medications, vacuum erection devices, and penile implants are among the treatments for ED post-prostatectomy.
3. Changes in Orgasm
- Dry Orgasm: Most men will experience dry orgasms, where there is little or no semen ejaculated, due to the removal of the prostate gland.
- Altered Sensation: Some men report changes in the sensation of orgasm or less intense orgasms.
4. Pain and Discomfort
- Post-Surgical Pain: Pain and discomfort in the surgical area are common immediately after the procedure.
- Long-Term Discomfort: Some men may experience long-term pelvic or perineal pain.
5. Psychological Impact
- Emotional Effects: Dealing with side effects like incontinence and ED can lead to feelings of embarrassment, frustration, and depression.
- Support and Counseling: Psychological support and counseling can be beneficial in managing these emotional impacts.
6. Hormonal Changes
- Testosterone Levels: Prostate removal can affect testosterone levels, leading to potential changes in mood, energy levels, and libido.
7. Risk of Hernia
- Incisional Hernia: There is a small risk of developing a hernia at the incision site, particularly after open surgery.
8. Lymphedema
- Swelling: If lymph nodes are removed during surgery, it can lead to lymphedema, a type of swelling in the legs or genital region.
9. Bowel Dysfunction
- Rare Complication: Some men may experience changes in bowel habits or function, although this is less common.
10. Cancer Recurrence Monitoring
- Regular Testing: Regular PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) tests are necessary to monitor for signs of cancer recurrence.
Embracing a New Normal: Life After Prostate Removal
Life after prostate removal, a journey many men face post-prostatectomy, involves adapting to changes and embracing a new normal. This period can be challenging, but with the right approach, support, and understanding, it can also be a time of positive transformation and adjustment.
1. Physical Adjustments
- Managing Side Effects: Post-surgery, men may experience urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Learning to manage these through pelvic floor exercises, lifestyle changes, and medical treatments is crucial.
- Regular Health Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider, including PSA tests, are essential to monitor for any signs of cancer recurrence and manage general health.
- Physical Activity: Gradually resuming physical activity is important. It aids in overall recovery and can improve strength, mood, and well-being.
2. Emotional and Psychological Well-being
- Processing Emotional Changes: It’s normal to experience a range of emotions, from relief to anxiety or sadness. Acknowledging these feelings and seeking support if needed is important.
- Support Systems: Leaning on support systems, including family, friends, and support groups, can provide emotional comfort and practical advice.
- Professional Counseling: For some, professional counseling or therapy can be beneficial in navigating the emotional aspects of recovery and adjustment.
3. Sexual Health and Intimacy
- Navigating Changes in Sexual Function: Changes in sexual function, including erectile dysfunction, can affect intimacy. Open communication with partners and exploring different ways to maintain intimacy are key.
- Medical Interventions: There are various treatments available for erectile dysfunction, including medications, vacuum devices, and penile implants. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help in choosing the right option.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: A healthy diet can aid in recovery and overall well-being. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or other relaxation practices can help manage stress and improve mental health.
5. Social and Recreational Activities
- Staying Socially Active: Engaging in social activities and hobbies can provide a sense of normalcy and enjoyment.
- Finding New Interests: Post-surgery can be a time to explore new interests or hobbies, which can be therapeutic and fulfilling.
6. Work and Daily Routine
- Returning to Work: The timeline for returning to work varies. It’s important to ease back into work and make adjustments as needed.
- Daily Routine Adjustments: Adapting daily routines to accommodate changes in physical and emotional health is part of embracing the new normal.
7. Long-Term Outlook
- Positive Perspective: Many men find that with time, they can adjust to their new normal and maintain a good quality of life.
- Continued Adaptation: It’s a continuous process of adaptation, learning, and growth. Embracing changes and seeking help when needed can lead to a fulfilling life post-prostate removal.
Conclusion

Navigating the journey of prostate removal and its aftermath is a multifaceted experience that encompasses physical health, emotional well-being, and lifestyle adjustments. While the prospect of undergoing prostatectomy and dealing with its side effects, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction, can be daunting, it’s important to recognize that these challenges are manageable with the right support and resources.
The journey post-prostate removal is not just about coping with the physical changes, but also about embracing a new normal. It involves a holistic approach that includes managing physical health through exercises, medical interventions, and regular health monitoring, as well as nurturing emotional well-being through support systems, counseling, and stress management techniques.
Adapting to changes in sexual health and intimacy is a significant aspect of this journey. Open communication with partners, exploring new dimensions of intimacy, and seeking medical advice for sexual dysfunction are crucial steps in maintaining fulfilling personal relationships.
Lifestyle modifications play a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of life after prostate removal. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and engaging in social and recreational activities contribute to overall well-being and a positive outlook.
Returning to work and daily routines requires patience and gradual adaptation. It’s important to listen to one’s body and make necessary adjustments to work and daily activities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Prostate Removal and Its Side Effects
-
What are the most common side effects after prostate removal?
The most common side effects include urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, changes in orgasm (such as dry orgasms), and potential psychological impacts like anxiety or depression. Pain and discomfort in the surgical area are also common immediately following the procedure.
-
How long does it typically take to recover from prostate removal?
Recovery time can vary widely depending on the type of surgery (open, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted), the patient’s overall health, and the presence of any complications. Generally, it can take several weeks to a few months to recover fully.
-
Can sexual function be restored after prostate removal?
Sexual function, particularly erectile function, can be affected after prostate removal. The extent of recovery depends on factors like age, baseline sexual function, and whether nerve-sparing techniques were used during surgery. Various treatments, including medications, vacuum devices, and penile implants, can help restore sexual function.
-
What can be done to manage urinary incontinence after surgery?
Management strategies include pelvic floor exercises (Kegel exercises), bladder training, medications, and in some cases, surgical interventions like sling procedures or artificial sphincters. Lifestyle modifications, such as fluid management and dietary changes, can also be helpful.
-
Is prostate removal always necessary for prostate cancer?
Not always. The necessity of prostate removal depends on several factors, including the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, the patient’s age and overall health, and personal preferences. Other treatment options may include radiation therapy, hormone therapy, or active surveillance.
-
Are there any long-term health issues associated with prostate removal?
Long-term issues can include persistent urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and changes in orgasm. Some men may also experience long-term pelvic pain. Regular follow-up care is important to monitor and address any long-term health issues.
-
How is life after prostate removal different?
Life after prostate removal can involve adjustments to manage side effects like urinary incontinence and changes in sexual function. Many men lead active, fulfilling lives post-surgery, but it often requires time to adapt and may involve changes in lifestyle and routines.
-
Can diet and exercise impact recovery after prostate removal?
Yes, a healthy diet and regular exercise can aid in recovery. A balanced diet helps in overall health and healing, while exercises, particularly pelvic floor exercises, can strengthen muscles involved in urinary control.
-
What support resources are available for men undergoing prostate removal?
Support resources include prostate cancer support groups, counseling services, and educational materials from healthcare providers and cancer organizations. Online forums and community groups can also offer support and information.
-
How often should I follow up with my doctor after prostate removal?
The follow-up schedule varies based on individual circumstances but typically includes regular visits to the urologist, PSA tests to monitor for signs of cancer recurrence, and discussions about managing any ongoing side effects.
Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects, Prostate Removal Side Effects,